Discover COM-B, one of the most influential analytical models in behavioral science.

What do you do for a living? Whatever you do, your goals surely depend on certain people behaving in a certain way.
– If you sell products and services, you want people to buy them.
– If you are a doctor, you might try to ensure that patients attend their appointments and follow prescribed treatments.
– If you are a counselor for the environment, you may be interested in getting citizens to travel more by bicycle and less by car.
But how can we encourage people to act in one way or another?
There are numerous behavioral change models that we can draw upon. Over the past 15 years, COM-B has been one of the most influential in finance, healthcare, and politics, among other areas.
1. What is COM-B?
The COM-B model was proposed by Susan Michie, Maartje M. van Stralen, and Robert West in their 2011 article “The behavior change wheel: A new method for characterizing and designing behavior change interventions”. The research analyzes 19 behavior change tools and offers a robust alternative whose effectiveness has been demonstrated in numerous interventions.
The COM-B model identifies three aspects that promote action: capability, opportunity, and motivation. In general, if we want someone to do something, we must promote their capability, opportunities, and motivation. For example, if we want our partner to play tennis with us, we will explain the rules of the game, tell them where and when we could play, and give them good reasons to want to join us.
2. The capability to act
Capability is the ability to perform an action. These can be physical or psychological:
– Physical capabilities are all those that enable our body to perform an action. They include strength, dexterity, agility, endurance, etc.
– Psychological capabilities are the knowledge, attention, memory, etc. required to act.
Returning to the previous example, for our partner to play tennis with us, they must be in good physical condition. If they have an ankle injury that prevents them from walking, they do not have the physical ability to play tennis with us.
Of course, you also have to know how to play and pay attention during the game. If you have suffered a recent tragedy and are unable to concentrate on the game enough to hit the ball, you are also unable to play tennis.
3. The opportunity to act
Opportunity refers to external factors that enable action. These factors are divided into physical and social factors.
– Physical opportunities are the spaces, products, and resources that make actions possible.
– Social opportunities are the set of cultural and normative aspects that promote behaviors.
To play tennis, I need physical space and a few things, such as rackets and balls. The tennis court in my neighborhood gives me the opportunity to play the sport. Without a tennis court (or similar space), it would not be possible to play tennis.
Furthermore, to play, I need to have access to the court. There is no point in having a tennis court if I am not permitted to enter it. Rules are important.
4. The motivation to act
Motivation is the set of mental phenomena that drive people to act. It can be automatic or reflective.
– Automatic motivation is spontaneous and even impulsive in nature.
– Reflective motivation is what occurs after conscious deliberation.
How can I motivate my partner to play tennis with me? I can show her photos and videos of celebrities playing tennis. When she sees them, she will want to play tennis too. Her motivation will be automatic.
I can also convince her that playing tennis is good for her health. I would have to offer her reasons, and she would have to weigh them up. If I managed to convince her, her motivation would be reflective.
5. The relationship between capability, opportunity, and motivation
Capability, opportunity, and motivation are not isolated elements, but rather affect and relate to each other in different ways.
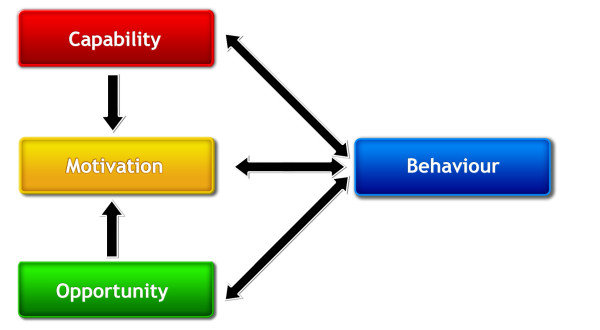
As the image (taken from the article cited) shows, capability and opportunity affect motivation. The better I am at something, the more I want to do it, especially when I can do it at a specific time and place. The better I am at playing the piano, for example, the more I want to play it, and the desire increases when I am in a room with a piano that I can play.
Furthermore, behavior itself impacts capability, motivation, and opportunity. The more I play the piano, the better I get at it, the more I want to play it, and the more opportunities I have to play it (at parties or recitals, for example).
For this reason, when we want to promote one of the aspects that leads to action, it is often advantageous to act on all three and nurture the synergies between them.
6. What is COM-B used for?
COM-B is a very useful behavioral model during the diagnostic phase of a behavioral intervention. It allows us to identify the barriers and levers that hinder or facilitate actions and check whether they affect ability, motivation, or opportunity. In this way, we can design specific interventions.
At BeWay, we often incorporate COM-B during the first stage of applying our behavior change methodology, BeMate.
7. How can we use it? The behavioral change wheel
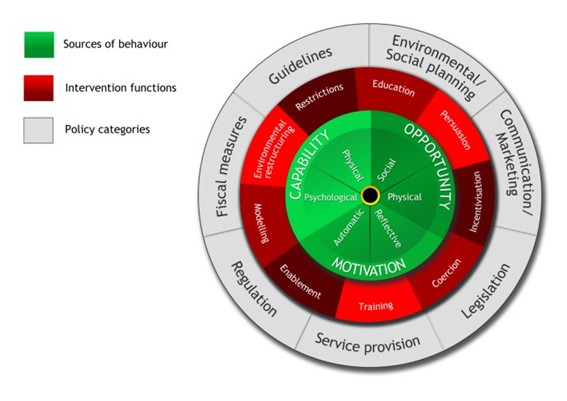
The COM-B model is part of a broader methodology: the behavior change wheel.
The behavior change wheel proposes 9 types of interventions to achieve the capability, opportunity, and motivation needed to carry out a behavior. The interventions are derived from the analysis of 19 academic articles.
The 9 types of interventions are:
– Education: This consists of increasing one’s knowledge or understanding of something.
– Persuasion: This involves using communication that induces emotions or stimulates actions.
– Incentives: This involves creating expectations of rewards.
– Coercion: This consists of creating expectations of costs.
– Training: It consists of developing skills.
– Restriction: This involves using rules to prevent or encourage behavior.
– Environmental restructuring: This involves modifying the physical or digital context.
– Modelling: This consists of offering examples of people whom others aspire to imitate.
– Enabling: This consists of providing the necessary resources and reducing barriers to enable something to happen.
Different interventions are useful for promoting different aspects of the COM-B model. Algunas favorecen la capacidad, otras la oportunidad y otras la motivación. Por ejemplo, la educación favorece la capacidad psicológica y la motivación reflexiva. Un curso de tenis en una escuela de secundaria puede servir tanto para enseñar a los alumnos cómo se juega como para motivarles a jugar.
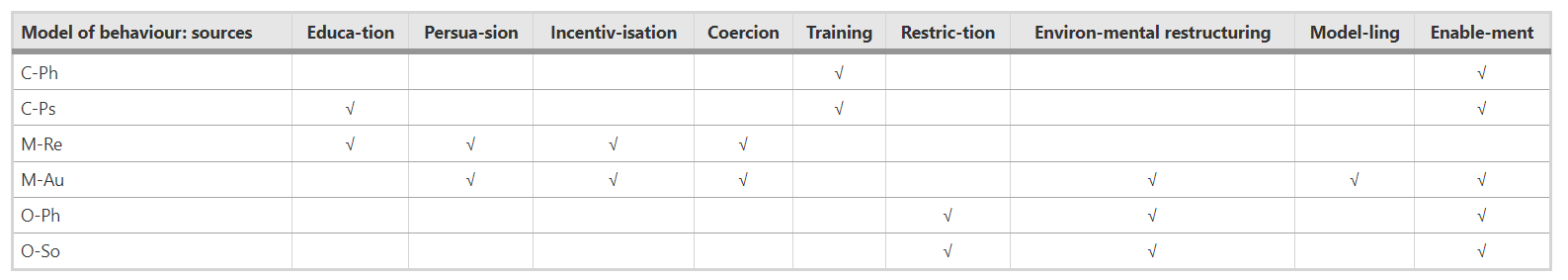
The following table indicates the most appropriate interventions in each case. C-Ph and C-Ps are physical and psychological capability. M-Re and M-Au are reflective and automatic motivation. And O-Ph and O-So are physical and social opportunity..
To carry out each of these interventions, the support of a general policy or strategy is needed. Michie and her colleagues distinguish seven.
– Communication and marketing: This involves using the media.
– The development of guidelines: This consists of creating documents that recommend or prescribe behaviors.
– Fiscal measures: This involves using the tax system to increase or reduce costs.
– Regulation: This consists of establishing rules or principles of conduct.
– Legislation: This involves changing the laws.
– Social or environmental planning: This involves designing and maintaining physical and social environments.
– Service provision: This consists of offering services.
The same type of intervention can be supported by different policies. For example, if we want to persuade people to use their cars less and bicycles more, we can do so with a communication campaign or by legislating to ban cars from city centers. The different policies are not, of course, mutually exclusive.
In this way, policies affect all three facets of behavior, but always through interventions. This is what is expressed in the wheel of behavior change.
Conclusions
The COM-B model of behavior change identifies three aspects that promote action: capability, opportunity, and motivation.
Capability is divided into physical and psychological ability, opportunity is both physical and social, and motivation is either automatic or reflective.
Capability, opportunity, and motivation are not isolated elements, but rather affect and relate to each other in different ways. For this reason, when we want to promote one of the aspects that leads to action, it is often advantageous to act on all three and nurture the synergies between them.
COM-B is a very useful behavioral model during the diagnostic phase of a behavioral intervention. For this reason, at BeWay we often use it during the first stage of BeMate.
The behavior change wheel proposes 9 types of interventions to achieve the capability, opportunity, and motivation needed to carry out a behavior. The same type of intervention can be supported by different policies.
Would you like to apply COM-B to identify areas for behavioral improvement in your company and design solutions based on scientific evidence? Contact us! We can help you!
Are you interested?
Get in touch!
